Latest Australia News
A Guide to becoming a Sovereign Individual
Knightsbridge is excited to announce the launch of our new club for…
PwC Australia Leaked Tax Info: Costly Consequences Ahead
Financial Impact of PwC Australia's Tax Scandal PwC Australia's admission to leaking…
Bitcoin Protects You Against Government Control
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency that is not subject to government…
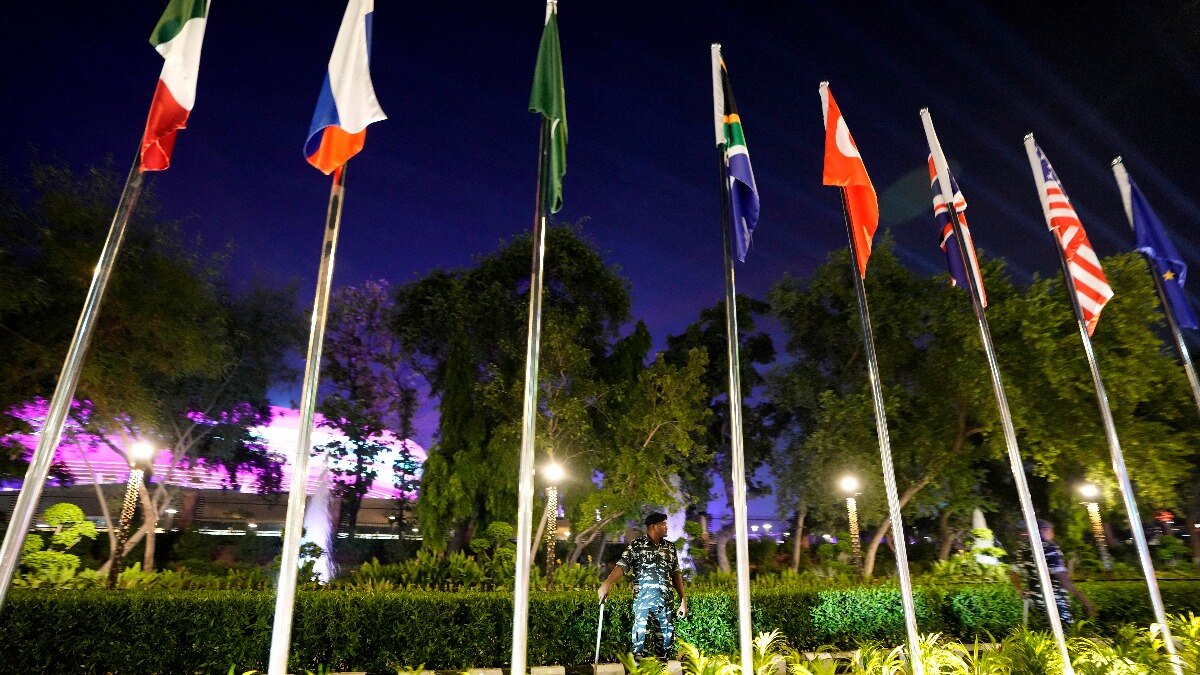
G20 Divided and Powerless
Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi seeks to forge consensus Saturday on a…
RCEP Free Trade Pack will Drive More Growth in Asia
The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) agreement came into force in the…
Inflation’s Storm Clouds are Forming Over US
#inflation #economy #recovery #GDP #VirusCasedemic $DIA $SPY $QQQ $RUTX $VXX The US…
Australia Will Lose Chinese Investors
China on Thursday said Australia's sudden scrapping of a Belt and Road…
Seaspiracy Exposes More Green Lies
Seaspiracy a documentary about ocean life, where a filmmaker, Ali Tabrizi, sets…
Some 2021 Regional Economic Outlooks
The year of 2021 will be critical for the whole world that…